It’s Official: Applegate Got Spammed. Now What?

Update: Applegate has been acquired by Hormel for $775 million. Rumors swirled back in February that Hormel is in talks to acquire Applegate Farms, the natural and organic meat company. As the news hit, the cry of “Nooooooooooooooo!” reverberated across the food movement.
Spam isn’t exactly a 21st century brand. Applegate very much is, meeting the needs of 21st century consumers who are looking for “free-from” foods.
But here is what I wrote back in February as those rumors hit, and here’s to Applegate helping Hormel to navigate this changing landscape.
So if Hormel can’t grow its mystery meat, is it any surprise that they are willing to purchase a company that is seeing 25% growth a year? These mega, 20th century brands, have one choice: embrace this new food economy or become obsolete.
And that embrace is increasingly looking like acquisitions.
Brands like Applegate have met the 21st century consumer where he or she stands: in the grocery store aisles with a family member battling any one of these conditions, looking for food that is “free from” artificial ingredients.
Many things are driving this food awakening and consumers’ quest for food that is free from things like allergens, artificial dyes, high fructose corn syrup and genetically engineered ingredients.
Our country is dealing with conditions like food allergies, asthma, diabetes, obesity and cancer at rates like never before.
And just as the announcement that General Mills would acquire Annie’s set off an emotional grenade, the news that Hormel might acquire Applegate has done the same.
There was an allergic reaction. The landscape of food is changing.
No one could have anticipated food ingredients designed by chemical companies that have been genetically engineered to produce their own insecticides. Nor could the industry have anticipated this food awakening, driven by the escalating rates of diseases and conditions like cancer, autism and food allergies and other conditions impacting the health of the people that we love.
Food allergies in our children are forcing us to read labels, as quickly as cancer diagnoses are forcing the same. No one would choose to be standing in the aisles of the grocery store, holding the hand of a child with food allergies or autism or managing a parent’s cancer diagnosis, yet that is where so many of us find ourselves today. We are being forced to read labels to protect the health of our loved ones, whether we want to read them or not. And sales of organic foods are soaring, as consumers try to eat a little bit better, a little bit cleaner and opt out of artificial ingredients. The U.S. branded organic and natural foods industry’s sales have been growing at a 12 percent compound rate over the last 10 years.
And while big food companies like Hormel and General Mills might have fought this for some time, they also aren’t stupid, and their job is to drive shareholder return. Sales of processed foods and conventional products that are pumped full of artificial growth hormones, artificial dyes and other artificial ingredients like GMOs are lackluster at best. The industry watches companies like Kellogg entrench and refuse to address this change in demand. What happens? Sales slump, and Kellogg’s reports a 136% plunge in profits.
It’s a slow death by artificial ingredients.
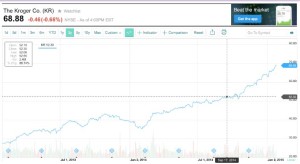
One look at the share price of Kroger or Chipotle tells the story of what happens to a company that expands into this ‘free from’ category: shareholders are rewarded.
Why wouldn’t a company want to enter this space in a meaningful way?
Change is hypocritical.
 Hormel has been part of the anti-labeling brigade. Led by the Grocery Manufacturers Association, they have been a member of the team of companies that have spent millions to keep consumers in the dark.
Hormel has been part of the anti-labeling brigade. Led by the Grocery Manufacturers Association, they have been a member of the team of companies that have spent millions to keep consumers in the dark.
That is their problem, as taking the position that a consumer does not have the right to know how her food is made, despite the fact that we are told if milk is pasteurized or if orange juice comes from concentrate, is undemocratic. It’s a freedom enjoyed by 60% of the world’s population.
Applegate has been an outspoken advocate for GMO labeling.
So just as there was outrage over the marriage between General Mills and Annie’s, the same sentiment is out there as Hormel eyes Applegate.
The reaction that consumers are having to the announcement is the fear that Hormel wrangles Applegate into submission. And while Hormel can operate Applegate with an expansive economy of scale and get their price to manufacture down, it’s not all altruistic. Hormel also knows that people are willing to pay more for Applegate’s products. It’s a way to diversify their portfolio, get better, higher margin products to market and increase Applegate’s availability in the marketplace. It’s good for business. They also see the writing on the wall, and it doesn’t contain the letters “G-M-O.”
The fear is that Applegate will fold, but this is where leadership and personal stories step in. Applegate’s CEO is a dad who led the company through extraordinary change, saw it burn to the ground and built it back up. He knows the supply chain, animal welfare issues and knows the demands of the financial world. He also knows what it is like to see someone that you love face serious health challenges. He knows that families around the country are experiencing these challenges every day.
And like the CEO of Stonyfield did when he expanded the brand and the reach of the yogurt company through its Danone partnership, perhaps Applegate found a partner to expand and capture economies of scale that the company couldn’t on its own. Stonyfield’s founder never backed down.
Just like General Mills buying into the organic movement through the purchase of Annie’s provided distribution and access to capital, Hormel buying into the movement could do the same.
Is consolidation the best answer? “These big food companies aren’t going to let anything else happen,” said one of the portfolio managers that I used to work with when I spoke with him today.
And right now, our food system is currently structured in a way that the costs of production for organic ingredients are disproportionately higher. It is structured this way at the federal level. It is not a level playing field for the organic industry. And when a company goes public, the way that Annie’s did in 2012, it is opening itself for an acquisition.
Since 2012, Applegate has been talking about how to grow, either through a public offering or some other way.
Does it mean that it will always be this way? That policy will always be this way? Not at all. Policy follows the money, and right now, the organic industry is growing while conventional is stagnant. The landscape of the food industry is changing at every level. Amazon is entering the retail space, online distribution companies are entering, too. Farmers market and community supported agriculture are taking off. Why? Because the grocery retail structure makes it hard for smaller brands to compete. They either have to sell out or buy in. It requires capital.
To hit the scale and scope of distribution that makes a product accessible and affordable to all Americans, companies have repeatedly sold themselves to a larger company: Stonyfield to Danone, White Wave to Dean Foods, Happy Family again to Danone. The list goes on.
Have these brands sold out? Or have the bigger brands bought into the organic movement? Stonyfield didn’t sell out. Happy Family didn’t either. Both companies were founded by people who have personally known how autism or cancer can impact a family.
Do I wish there were other ways for these companies to scale? And that the food industry had a level playing field for organic companies? Absolutely. There is nothing that I would rather have seen then Annie’s, White Wave, Hain Celestial and other organic brands become the iconic brands of the 21st century. Our generation’s iterations of Kraft, General Mills and Pepsi. To see Applegate replace Hormel as the iconic brand.
Perhaps this is the first iteration towards that. But right now the cost structure is prohibitive. We haven’t financed a healthy food system at the federal level. If farmers want to grow organic crops, they lose the crop insurance protection programs, they lose subsidies and they lose marketing support. Is that financially viable? If you throw animal husbandry and animal welfare into that, you’ve got an even more complicated issue.
The food movement is not going away. Demand for food that is ‘free from’ artificial ingredients like food dyes, GMOs, high fructose corn syrup and other ingredients is not a fad, because cancer, autism and food allergies are not fads. We are seeing a fundamental shift in the way that Americans buy food, because we are sick.
General Mills obviously recognized that. Hormel does, too. They are hedging with these acquisitions, balancing their portfolio. The key is to not compromise the integrity of the Applegate’s brand in the process. Creative destruction is an economic term trumpeted by a man named Joseph Schumpeter. And change, in these early stages, often looks like hypocrisy. It often looks destructive. The question becomes: what is the long term objective here? Is it really to destroy a brand? No, it’s to capture its market share, its margins and expand into the category.
So how could this play out?
A look back at other historic acquisitions in the food industry gives us a feel for how this could play out, because if the share prices of White Wave and other organic companies are any indication today, this consolidation stage will continue.
In 1985, Philip Morris Cos. became a holding company and the parent of Philip Morris Inc. and bought General Foods. The acquisition of Kraft Foods came in 1988. In 2001, Kraft Foods spun out of Phillip Morris and launched an IPO for 11.1% of the company that raked in $8.7 billion, making it the 2nd largest IPO in American history at the time.
General Mills could spin Annie’s back out in a few years time, like Philip Morris did with Kraft or like Dean Foods did with White Wave. Hormel could do the same with Applegate. Maybe that IPO isn’t that far out, and we could see the ticker symbol “MEAT” in 2020. They would drive enormous shareholder value if they stay true to the brand.
If they don’t, there are plenty of examples of fallout in the food industry. From Kellogg’s, to the companies that made pink slime to those that put yoga mat material in their buns. Shareholders suffer if companies don’t response to the 21st century online consumer.
We live in a day and time where online bullying can take many forms. At the end of the day, no one misses a beat, and companies that think they can pull a fast one on the consumer are quickly proven wrong.
Refinance Food
We have financed a food system that gives food companies the incentive to use the cheaper ingredients. The cost of producing organic ingredients is disproportionately higher than producing conventional, genetically engineered crops. On top of that, farmers that choose to grow organic crops don’t get the crop insurance programs and marketing support programs. In other words, their entire cost of production is higher. That hammers all of us. It hammers food companies trying to do the right thing.
And as much as any of us want to romanticize food, right now, this is our current capitalist structure, and until we refinance the food system, this won’t be the first of these acquisitions.
What if the cost of production were the same? What if farmers, regardless of what they choose to plant on their farms, could receive crop insurance programs and marketing support? What if food companies, regardless of what they choose to use in their products, had to label their ingredients as genetically engineered or not.
Right now, there is economic discrimination. Costs are disproportionately higher for those who want organic food, from the farmers growing it to the food companies using it to the families eating it.
Does anyone want it this way? Does General Mills? Do our farmers? Do our families?
But we weren’t given a choice.
Right now, our taxpayer resources are used to support the food system dependent on GMOs and chemicals. What if at the voting booth, we got to check a box?
Do you want your taxpayer resources to support the food system? And if yes, which would you rather see support given to farmers growing organic ingredients? To food companies using them?
How do we want our tax dollars to work in the food system?
What would Hormel choose if price weren’t an issue? If there were an economic equilibrium, which ingredients would Hormel choose? What livestock feed? Genetically engineered or organic? And why haven’t we structured our food system with this kind of pricing parity?
Right now, no one has been given the choice because of the financial structure executed at the federal level through the crop subsidy programs, the crop insurance programs and the marketing support programs. They only go one way.
Is this acquisition a symptom of that unhealthy financial structure?
It wouldn’t be a hostile takeover. Applegate would enter into it like Stonyfield did with Danone or White Wave did with Dean Foods.
The question is whose compass is stronger? What will consumers do to send the message to Hormel that being part of the anti-labeling campaign is detrimental to shareholders?
Like Annie’s did, Applegate has the wind at its back. Hormel knows that. Consumers want “free from” food. Food that is “free from” artificial ingredients, artificial dyes, growth hormones and genetically engineered ingredients. One look at the share price of Chipotle tells that story.
As more and more companies enter the organic space, either through new products or through acquisitions, it again begs the question: is the Grocery Manufacturers Association a relic of the 20th century? If this organization is not working to meet the needs of its member companies, should it still exist in its current form? Or should a new organization, let’s call it the Food Production Association, be formed to meet the evolving needs of these brands in the 21st century?
Change at its very core begins with hypocrisy.
If Hormel chooses to make a strategic shift and follow Applegate into an industry with a 12% compound annual growth rate, capitalizing on Applegate’s 25% growth, delivering a portfolio increasing full of “free from” foods, shareholders will be rewarded. The rates of cancer, autism, food allergies and other conditions aren’t declining. This food awakening isn’t a fad.
Applegate has the potential to be a powerful compass for Hormel. If the companies are serious about their commitment to the 21st century consumer and their shareholders, they should step away from the Grocery Manufacturers Association’s anti-labeling campaign and join the consumer where she stands: in the grocery store aisles, reading food labels while holding the hand of a loved one with allergies, autism, EoE, cancer, diabetes or any one of the conditions impacting our families today and deliver exactly what she wants: food that is “free from” artificial ingredients and information about how she can protect the health of her family.
It’s up to Hormel if they continue to operate with a 20th century mentality or if they will move into the 21st century with the consumer and Applegate as a compass. It’s a big ask, but it’s important to look at what can happen if they don’t follow Applegate’s lead. With a 136% profit slump, Kellogg has an entrenched story to tell.
Applegate’s goal is to change the way we eat. It’s already happening.
It’s up to Hormel to decide what story will be theirs.
The smartest thing Hormel could do for its shareholders is to use Applegate as a compass and dump the junk. Instead of spamming Applegate, shareholders should pay attention to why this acquisition makes sense in the first place: demand is shifting. 21st century consumers want “free-from” food. No amount of Spam is going to change that.





